When it comes to alcohols, methanol and ethanol often take center stage. But do you know the key differences between these two chemical compounds?
You might think they’re similar because they both fall under the alcohol category, yet they serve vastly different purposes and have distinct properties. Imagine the power of knowledge when you can confidently distinguish methanol from ethanol, whether you are fueling engines, crafting homemade beverages, or ensuring safety in your everyday life.
You’ll uncover the unique characteristics of each, learn about their practical applications, and discover why understanding these differences is crucial. Stick with us to ensure you make informed decisions, whether you’re working in a lab or simply curious about the world of alcohols. Your journey into the fascinating world of methanol and ethanol starts here.
Credit: rayeneh.com
Chemical Composition
Methanol and ethanol are both alcohols, but they differ in structure. Their unique chemical composition influences their applications and properties. Understanding these differences can help in determining their usage in various industries.
Molecular Structure
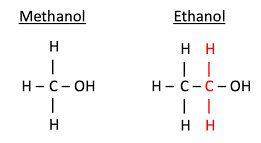
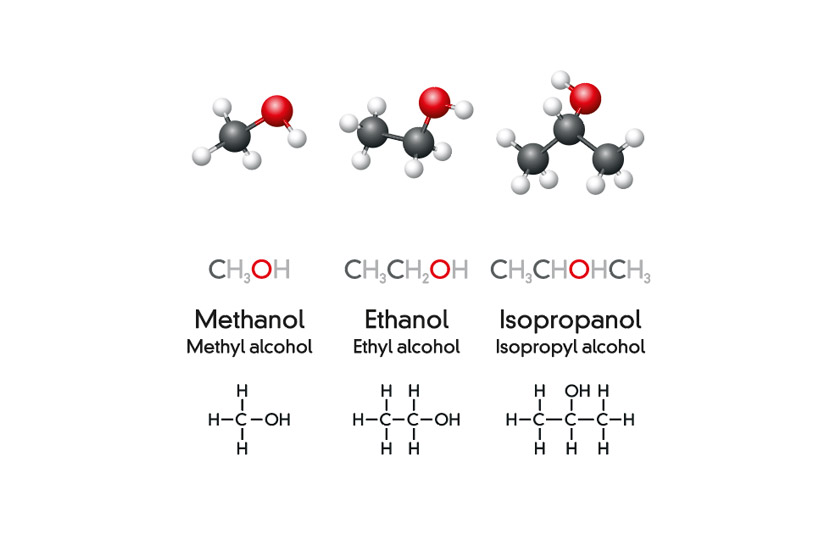
Methanol has one carbon atom, forming a simple structure. Its formula is CH3OH. Ethanol, in contrast, contains two carbon atoms. Its formula is C2H5OH. This extra carbon gives ethanol a slightly larger molecular size. Both contain a hydroxyl group, which is crucial for their alcohol classification.
Chemical Properties
Methanol is more volatile than ethanol. It evaporates quickly, making it useful for fuel applications. Ethanol, with its extra carbon, burns cleaner. It produces less toxic by-products. Methanol is poisonous if ingested. Ethanol is safer and used in beverages. Both are flammable but have different combustion characteristics. Ethanol’s higher energy content makes it a preferable fuel source.
Production Methods
Methanol and ethanol are two significant alcohols with distinct production methods. Understanding their synthesis and fermentation helps in grasping their industrial applications. Let’s dive into how these alcohols are produced.
Methanol Synthesis
Methanol is primarily produced from natural gas. The process involves converting methane to syngas, a mixture of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide. This conversion happens through steam reforming. In steam reforming, methane reacts with steam at high temperatures. The resulting syngas undergoes a catalytic reaction. This reaction occurs in the presence of a catalyst, usually copper or zinc oxide. The catalyst speeds up the conversion to methanol. The process is efficient and widely used in the chemical industry.
Ethanol Fermentation
Ethanol is commonly produced through fermentation. Fermentation involves the conversion of sugars to alcohol. Yeasts play a crucial role in this process. These microorganisms consume sugars from plants like corn or sugarcane. During fermentation, yeasts convert sugars into ethanol and carbon dioxide. The process takes place in large fermentation tanks. The resulting ethanol is then distilled to increase purity. This method is popular in the beverage and biofuel industries. It relies on renewable resources, making it environmentally friendly.
Uses And Applications
Methanol and ethanol are versatile chemicals. They serve numerous purposes across various industries. Understanding their uses and applications can help distinguish their importance. Each has unique roles, from industrial to pharmaceutical sectors.
Industrial Uses
Methanol is a key component in manufacturing. It is used to produce formaldehyde and other chemicals. This makes it vital in the creation of plastics and resins. Ethanol is widely used in the production of alcoholic beverages. It also serves as a solvent in laboratories and manufacturing.
Fuel Applications
Methanol is a potential fuel alternative. It is used in some types of racing cars. It can also blend with gasoline to reduce emissions. Ethanol is commonly found in fuel blends. Known as E10 or E85, these blends help reduce air pollution. Ethanol is renewable, making it popular in sustainable energy initiatives.
Pharmaceutical Uses
Ethanol is significant in the pharmaceutical industry. It is used as an antiseptic and disinfectant. Ethanol is found in many medicinal solutions. Methanol has limited use due to its toxicity. Careful handling is required when used in pharmaceuticals. It serves as a solvent in specific drug formulations.
Credit: berkshire.com
Safety And Toxicity
Understanding the safety and toxicity of methanol and ethanol is crucial. Both chemicals have distinct properties that influence their safety levels. Knowing these differences helps in handling them properly. Each has its own set of risks and environmental impacts.
Health Risks
Methanol is highly toxic if ingested or inhaled. It can lead to blindness and even death. Ethanol, found in alcoholic drinks, is less toxic. But, excessive consumption can harm the liver and brain. Both require careful handling to prevent health issues.
Environmental Impact
Methanol poses significant environmental risks. It can contaminate water sources and harm aquatic life. Ethanol is more environmentally friendly. It biodegrades quickly and has less impact on ecosystems. Choosing ethanol over methanol reduces environmental harm.
Economic Factors
Methanol and ethanol are both important for the economy. Methanol is cheaper to produce but less efficient. Ethanol costs more but offers better energy output, impacting fuel choices.
Economic Factors When comparing methanol and ethanol, understanding the economic factors is crucial. These factors influence everything from production to market dynamics. Let’s dive into the specifics to see how they affect your choices.Cost Of Production
The cost of producing methanol and ethanol varies significantly. Methanol is typically cheaper to produce because it is derived from natural gas, a relatively abundant resource. This often results in lower production costs compared to ethanol. Ethanol production, on the other hand, involves agricultural processes. It’s primarily made from corn or sugarcane, both of which require extensive farming. This dependency on crops can drive up costs, especially if there are poor harvests. Have you ever thought about how seasonal changes might affect ethanol costs? A drought year could dramatically increase prices, influencing your budget.Market Demand
The market demand for methanol and ethanol plays a significant role in their economic viability. Methanol is widely used in industries such as automotive and chemical manufacturing, which drives consistent demand. Ethanol enjoys high demand in the fuel industry, especially as a biofuel additive. Many countries encourage its use to reduce carbon emissions, boosting its market presence. However, demand can shift based on government policies and consumer trends. For instance, a push for greener energy sources could increase ethanol demand, but what happens if another renewable source becomes more popular? Understanding these market dynamics can help you make informed decisions. Whether you’re investing in production or simply considering which fuel to use, keeping an eye on these factors is essential.
Credit: www.wikihow.com
Future Prospects
The future of methanol and ethanol holds promise. Both fuels are key players in the transition to cleaner energy. Understanding their potential can guide sustainable choices. Let’s explore their future prospects through innovations and sustainability.
Innovations In Production
Production methods for methanol and ethanol are evolving. New technologies aim to increase efficiency. Methanol production is focusing on reducing carbon footprint. Biomass conversion is a promising method.
Ethanol production is also seeing advancements. Second-generation biofuels use non-food crops. This reduces competition with food supply. Both fuels are benefiting from research and development. Enhanced production methods will play a crucial role.
Sustainability Concerns
Sustainability is a major concern for both fuels. Methanol production from fossil fuels raises questions. Shifting to renewable sources can address these concerns.
Ethanol is often seen as more sustainable. But, land use and water consumption are issues. Balancing production with environmental impact is crucial. Both fuels must address these challenges for a sustainable future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Primary Uses Of Methanol?
Methanol is mainly used as an industrial solvent, antifreeze, and fuel.
How Does Ethanol Differ From Methanol?
Ethanol is safe for consumption in beverages. Methanol is toxic and used in industrial applications.
Why Is Methanol Considered Dangerous?
Methanol is toxic. Ingesting or inhaling it can cause serious health issues or death.
Can Ethanol Be Used As Fuel Like Methanol?
Yes, ethanol is used as a biofuel. It’s blended with gasoline for cleaner combustion.
What Are The Environmental Impacts Of Methanol And Ethanol?
Both can reduce emissions. Ethanol is renewable, but methanol production can impact fossil fuel use.
Conclusion
Choosing between methanol and ethanol depends on your needs. Both have unique features. Methanol is toxic but cheaper. Ethanol is safer but costs more. Consider their uses and safety. Make informed decisions based on your priorities. Understanding the differences helps in selecting the right one.
Keep in mind their environmental impact. Methanol and ethanol both have pros and cons. Evaluate carefully before using. Whether for fuel or other applications, knowledge is key. Choose wisely for your project. Always prioritize safety and efficiency. Your choice affects results and sustainability.
Make the best decision for your needs.





