Imagine your home, a sanctuary from the outside world, where comfort and efficiency reign supreme. But have you ever considered how your roof plays a crucial role in this?
The choice between a hot roof and a cold roof might seem trivial, yet it can significantly impact your living space’s temperature, energy bills, and overall comfort. Whether you’re planning to build a new home or upgrade your current one, understanding the differences between these two roofing systems is vital.
Picture yourself enjoying a cozy winter evening indoors or a refreshing summer day without breaking a sweat. The right roofing choice can turn these visions into reality. As you delve deeper into the intricacies of hot roofs and cold roofs, you’ll discover how your decision can lead to more efficient energy use, reduced costs, and enhanced comfort. So, are you ready to explore how the right roof can transform your home into a haven of comfort? Keep reading to uncover which option is best suited for your needs and how it can improve your everyday life.

Credit: colonyroofers.com
Hot Roof Concept
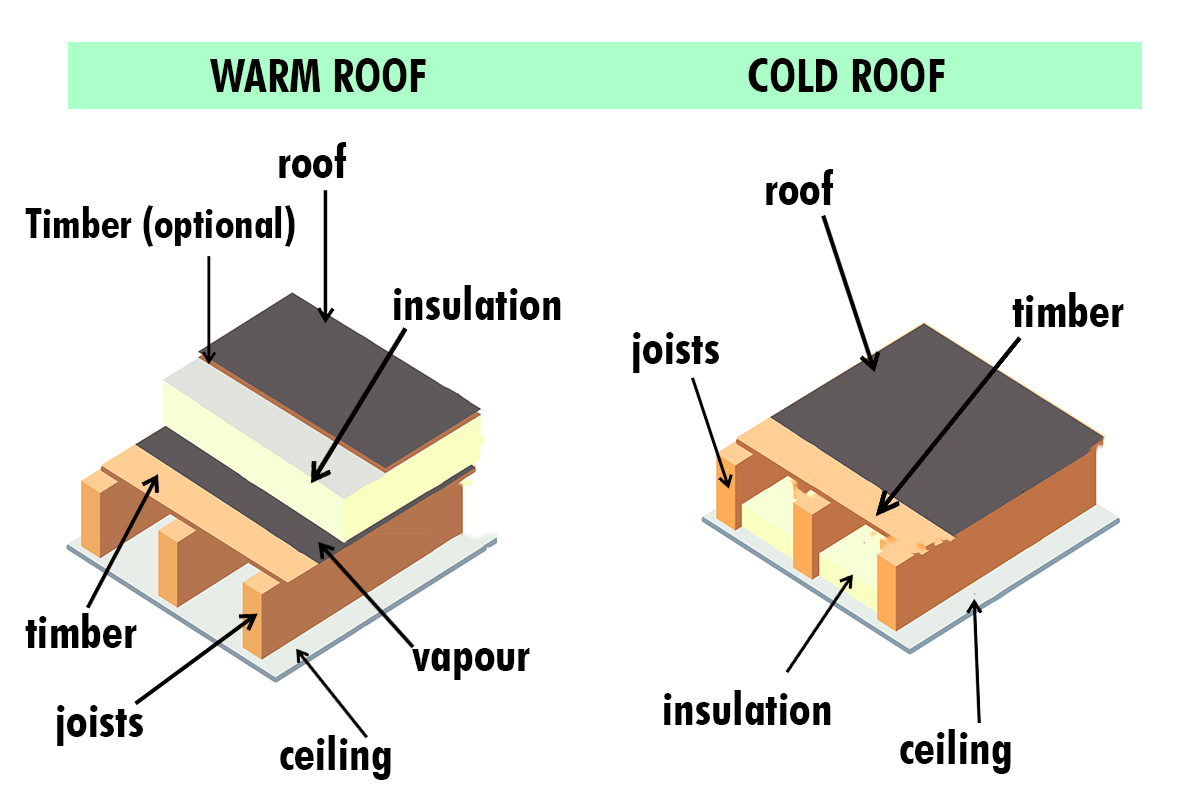
Comparing hot roofs and cold roofs involves understanding insulation and ventilation. Hot roofs insulate beneath the roof deck, reducing energy loss. Cold roofs use attic ventilation to maintain cooler temperatures, preventing moisture buildup. Each system offers unique benefits, focusing on energy efficiency and climate suitability.
In the world of roofing, the hot roof concept is gaining traction for its energy efficiency and modern appeal. Imagine a roof system where the insulation is placed directly under the roof deck, with no ventilation space. This approach can significantly affect your home’s temperature regulation and energy bills.Definition And Characteristics
A hot roof is characterized by the lack of a ventilated attic space. Instead, the insulation is installed directly against the roof deck. This design ensures that the attic space is as warm as the rest of the house, which can help reduce energy loss. This type of roof is particularly beneficial in areas with extreme weather conditions. It can help maintain a stable temperature inside your home. This could potentially lead to savings on your energy bills.Materials Used
The materials used in a hot roof system are crucial for its effectiveness. Spray foam insulation is the most common choice. It expands to fill gaps, providing excellent thermal protection. Another option is rigid foam insulation, which is known for its durability and ease of installation. These materials work together to create a seamless barrier against temperature fluctuations. You might wonder if these materials are right for your home. Consider the climate you live in and your energy efficiency goals.Installation Process
Installing a hot roof involves placing insulation directly beneath the roof deck. This process requires precision to ensure no gaps are left. If you’re handy, you might be tempted to try this yourself, but professional installation is often recommended. The installation can be more complex than a traditional cold roof due to the need for airtight sealing. Proper installation is key to preventing any potential moisture issues. Have you considered how this might impact your home’s energy efficiency? A well-installed hot roof can be a game changer, potentially leading to lower heating and cooling costs. Overall, the hot roof concept is an innovative approach to roofing that offers numerous benefits. It’s worth considering if you’re aiming for a more energy-efficient home. Would you make the switch to a hot roof?Cold Roof Concept
The cold roof concept is gaining popularity in various regions. This method helps maintain a building’s temperature efficiently. It offers a contrast to the hot roof approach. Cold roofs are designed to keep the attic space cool. This aids in reducing energy costs and prolonging roof life.
Definition And Characteristics
A cold roof is a roofing system that keeps the attic cool. It features a layer of ventilation beneath the roof deck. This allows air to circulate, preventing heat buildup. Cold roofs are effective in climates with extreme temperatures. They help in maintaining a steady indoor environment.
Materials Used
Cold roofs use materials that enhance ventilation. Common materials include vented roof tiles and breathable membranes. These materials allow air to pass through easily. Insulation boards are often used to improve efficiency. Reflective materials can also be part of the design.
Installation Process
The installation of a cold roof involves several steps. First, a layer of insulation is placed between rafters. Next, a breathable membrane is added on top. This allows moisture to escape, preventing dampness. Ventilation tiles are then installed to promote airflow. Finally, the roof covering is laid over the entire structure.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Choosing between a hot roof and a cold roof impacts your home’s energy efficiency. Both roofing systems offer unique benefits. Understanding these differences can help you make an informed decision. Let’s explore how each roof type influences thermal performance, costs, and the environment.
Thermal Performance
Hot roofs allow heat to penetrate into the attic. This can increase indoor temperatures. They usually have less insulation than cold roofs. Cold roofs, on the other hand, have better insulation. They keep heat from entering the attic. This helps maintain a stable indoor temperature.
Impact On Heating And Cooling Costs
Hot roofs may lead to higher cooling bills in summer. The increased attic temperature forces air conditioners to work harder. Cold roofs can reduce cooling costs. They limit heat entry into the home. In winter, hot roofs may offer slight heating cost savings. Yet, cold roofs provide consistent energy savings year-round.
Environmental Considerations
Cold roofs contribute to lower energy consumption. This reduces greenhouse gas emissions. They often use materials that reflect sunlight. This helps decrease urban heat island effects. Hot roofs might use more energy. Thus, they can have a greater environmental impact. Opting for a cold roof can support sustainable living.
Credit: www.buyinsulationonline.co.uk
Climate Considerations
Choosing between a hot roof and a cold roof affects energy efficiency and climate control. Hot roofs absorb heat, warming the building, while cold roofs reflect sunlight, keeping interiors cooler. Each option impacts heating and cooling costs and is influenced by regional climate conditions.
When considering a roofing system, climate plays a significant role in deciding between a hot roof and a cold roof. Your geographical location affects the performance of these roofing options. Understanding how each roof type interacts with the climate can save you money and increase comfort.Suitability In Different Regions
Hot roofs are more suited for colder regions. They prevent heat from escaping, which is essential in places where winters are long and harsh. On the other hand, cold roofs work best in hotter climates. They reflect sunlight, which keeps your home cool during scorching summer months. Have you ever noticed how some homes stay cooler in summer without air conditioning? That’s often the power of a well-designed cold roof.Impact Of Seasonal Changes
Seasonal changes impact roofing performance significantly. A hot roof in winter helps maintain a stable indoor temperature, reducing heating costs. But during summer, the same hot roof could make your home feel like an oven, leading to higher air conditioning bills. Cold roofs excel during summer, but in winter, they might not provide the warmth you need. Imagine having a roof that adapts like your wardrobe—changing with the seasons. While we aren’t there yet, knowing your region’s climate can help you choose the most effective roofing system. Selecting the right roof type isn’t just about today. Consider how your choice will perform throughout the year. Would you prefer lower heating costs in winter or a cooler home in summer? Your answer might just lead you to the perfect roofing solution.Cost Implications
Choosing between a hot roof and a cold roof affects your budget. Hot roofs may lower energy costs but require more insulation. Cold roofs are cheaper upfront but might lead to higher heating expenses over time.
When considering the cost implications of choosing between a hot roof and a cold roof, it’s essential to weigh both the initial investment and the potential for future savings. Your budget will guide your decision, but understanding the financial impact over time can make a big difference. Let’s dive into the details and see how each option stacks up.Initial Installation Costs
The upfront costs of a hot roof can be higher due to the need for additional insulation. This type of roof requires specialized materials and skilled labor, which can increase your initial expenses. However, some homeowners find the investment worthwhile for the energy efficiency benefits. On the other hand, a cold roof usually involves lower initial costs. Since it doesn’t require extra insulation layers, the material and labor costs are often more budget-friendly. If you’re looking for a cost-effective option right out of the gate, a cold roof might be more appealing.Long-term Savings
With a hot roof, you could see significant savings on your energy bills over time. The additional insulation helps maintain a consistent indoor temperature, reducing the need for heating and cooling. This can lead to lower utility bills and can offset the initial investment over the years. A cold roof may not offer the same level of energy savings but can still be cost-effective in the long run. By allowing natural ventilation, it can help prevent moisture buildup, reducing the risk of mold and prolonging the lifespan of your roof. This can save you money on repairs and maintenance down the line. Consider your climate and lifestyle when evaluating these options. If you live in an area with extreme temperatures, the long-term savings of a hot roof might outweigh the upfront costs. On the other hand, if your climate is mild, a cold roof could be a better fit for your budget. What factors influence your decision when weighing costs and benefits? Are you more focused on immediate savings, or are you thinking long-term? Your priorities will shape the best choice for your home.
Credit: benjaminobdyke.com
Maintenance And Durability
Understanding the maintenance and durability of hot and cold roofs is vital. Homeowners often seek roofing solutions that last long and require minimal upkeep. Each roof type has unique characteristics affecting its lifespan and care needs. Let’s explore common maintenance practices and expected lifespan for both roof types.
Common Maintenance Practices
Hot roofs need frequent inspections to check for leaks and damage. Regularly cleaning debris off the roof surface is crucial. It prevents water pooling, which can weaken the roof structure. Cold roofs require insulation checks to ensure efficiency. Keeping the ventilation system clear is important. It maintains airflow and prevents moisture build-up.
Expected Lifespan
Hot roofs typically last 20 to 30 years. Their lifespan depends on material quality and installation. Regular maintenance prolongs their durability. Cold roofs may last up to 50 years. They often have a longer lifespan due to their design. Proper insulation and ventilation are key to their longevity.
Case Studies
Explore the differences between hot roofs and cold roofs through detailed case studies. Understand how insulation and ventilation impact energy efficiency and indoor comfort. Discover practical insights for choosing the best roofing solution for your needs.
When considering the best roofing system for your building, diving into real-world examples can be enlightening. Case studies of both hot and cold roofs highlight the practical benefits and challenges of each option. These stories provide a clear picture of how different roofing systems perform in various settings and climates. Understanding these can guide your decision-making process and help you choose the best option for your needs.Residential Applications
In a recent study, a family in Minnesota faced skyrocketing heating bills during the winter. They opted for a hot roof system to address this. After installation, they noted a significant reduction in energy costs. The attic, now part of the home’s thermal envelope, stayed warmer. This not only improved their energy efficiency but also increased the comfort level of their home. The family reported fewer drafts and more consistent indoor temperatures. On the other hand, a household in Southern California chose a cold roof. Their goal was to tackle the intense summer heat. The reflective surface of the cold roof successfully reduced the amount of heat entering the home. This change led to lower air conditioning costs. The family enjoyed a cooler home environment without relying heavily on their HVAC system. They found the cold roof to be an effective solution for their climate.Commercial Applications
A warehouse in Texas faced challenges with heat management. They experimented with a hot roof system to enhance insulation. The results were promising, as the internal temperature remained stable even during extreme heat. The building’s energy expenses dropped. Employees also noticed a more comfortable working environment. The business saw this as a win-win: cost savings and improved employee satisfaction. Conversely, a retail store in New York City went for a cold roof. Their priority was to minimize cooling costs during hot summers. They found that the cold roof’s reflective capabilities significantly cut down on energy usage. Customers and staff appreciated the cooler store atmosphere. The store owners observed increased foot traffic, attributing it to the comfortable shopping experience. This case highlighted how a roofing choice can impact both operational costs and customer satisfaction. Have you considered how your choice of roofing might influence your energy bills or the comfort of your space? Reflecting on these case studies, it’s clear that the right roofing system can make a substantial difference. Whether it’s a hot or cold roof, aligning your choice with your specific needs and climate is crucial. What’s your next step in optimizing your roofing?Future Trends
Exploring future roofing trends reveals the debate of hot roofs versus cold roofs. Hot roofs improve energy efficiency by sealing attic spaces, while cold roofs reflect sunlight to reduce heat absorption. Choosing between them depends on climate needs and energy goals.
The future of roofing leans towards innovation and sustainability. Hot roofs and cold roofs are evolving. They are adapting to new technologies and environmental needs. Understanding these trends can guide homeowners and builders. They can make informed decisions about roofing choices.Innovations In Roofing Technology
Roofing technology is advancing rapidly. Smart roofs are gaining popularity. These roofs use sensors. They monitor weather conditions and energy usage. Smart roofs improve energy efficiency. They also enhance roof durability. Lightweight materials are another innovation. They are easy to install and reduce structural load. These materials offer improved insulation. They help in maintaining indoor temperatures. Transparent solar panels are also emerging. They integrate with roofs seamlessly. They provide energy without compromising aesthetics.Sustainability Trends
Sustainability is a key focus in roofing. Green roofs are becoming common. They are covered with vegetation. Green roofs improve air quality. They also provide natural insulation. Recycled materials are also in trend. They reduce waste and environmental impact. Cool roofs are gaining attention too. They reflect more sunlight. This reduces heat absorption. Cool roofs help in lowering cooling costs. They contribute to energy conservation. Sustainable roofing benefits both the environment and homeowners. It promotes energy savings and reduces carbon footprint.Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Difference Between A Hot Roof And A Cold Roof?
A hot roof has no ventilation, while a cold roof is ventilated. This affects insulation and energy efficiency.
Which Roof Type Is More Energy Efficient?
A cold roof is generally more energy efficient. It reduces heat buildup, saving on cooling costs.
Is A Hot Roof Suitable For All Climates?
Hot roofs are best for cold climates. They retain heat, which is beneficial in chilly weather.
Do Cold Roofs Help In Preventing Mold?
Yes, cold roofs prevent mold. Ventilation reduces moisture buildup, which discourages mold growth.
Are Cold Roofs More Expensive To Install?
Cold roofs can be costlier due to ventilation needs. But they save on energy over time.
Conclusion
Choosing between a hot roof and a cold roof depends on your needs. Hot roofs are great for insulation and energy efficiency. They can save on heating costs. Cold roofs reduce cooling needs and prevent heat buildup. They help keep homes cooler in summer.
Consider climate and budget when deciding. Both options offer unique benefits. Balance your needs with local weather. Consult a roofing expert if unsure. This ensures the best choice for your home. A well-informed decision leads to long-term satisfaction.





