Plugging a generator directly into a wall socket is unsafe and can cause serious hazards. This method, known as backfeeding, is illegal.
Generators are essential in providing power during outages, making them a popular choice for emergency preparedness. Yet, the method of connecting them to your home’s electrical system requires careful consideration. Safety protocols and proper equipment are paramount to avoid electrical fires, damage to appliances, or endangering utility workers.
Backfeeding by plugging a generator into a wall socket bypasses these critical safety measures. It’s crucial to understand the risks and seek safe alternatives, like installing a transfer switch, to harness the benefits of a generator without compromising safety. The right approach ensures that your reliance on a generator during power outages is both effective and secure.
Credit: tikweld.com
The Risks Of Improper Generator Use
The Risks of Improper Generator Use can lead to serious issues. Connecting a generator directly to your home’s wiring can be risky. Let’s explore these risks in detail.
Safety Hazards
Using generators the wrong way can cause fires. Carbon monoxide poisoning is another risk. Always read the manual before using a generator.
- Fire: Sparks can ignite nearby materials.
- Gas: Generators produce carbon monoxide. This gas is deadly.
- Electric Shock: Wet conditions can lead to shocks.
Electrical Overloads
Plugging a generator into a wall socket can overload circuits. Overloads damage electronics and appliances. They can even start fires.
| Issue | Result |
|---|---|
| Overload | Fried circuits |
| Power Surge | Broken appliances |
| Fire | Property damage |
Generator Basics
Welcome to the world of generators! Understanding how these powerhouses work is key to safe and efficient use. Let’s explore the essentials of generators and their various types available today.
How Generators Work
Generators are vital for creating electricity without a grid. They convert fuel into power, keeping lights and appliances running during outages. A generator’s engine burns fuel, usually gas, propane, or diesel. This engine turns a turbine, creating usable electricity for homes or businesses.
Types Of Generators Available
Various generators cater to different needs. From portable units to standby systems, choices abound. Let’s look at the common types:
- Portable Generators: Great for camping or job sites. They are small and easy to move.
- Inverter Generators: They are quiet and efficient. Perfect for sensitive electronics.
- Standby Generators: Installed permanently. They start automatically during power cuts.
- Industrial Generators: These are large. They power big buildings and critical systems.
Choosing the right generator depends on your needs. Consider size, fuel type, and power output. Stay powered up safely and efficiently!
Understanding Wall Sockets
Understanding Wall Sockets is essential before plugging in any device. This includes generators. Wall sockets in your home carry electricity. They power up your devices.
Standard Household Wiring
Every home has a network of wires. These wires carry electricity. They connect to wall sockets. Each wire has a purpose. One wire is hot. It brings electricity in. Another is neutral. It sends electricity back. A third wire is the ground. It makes using electricity safe.
Socket Capacity And Limitations
Sockets have power limits. These limits protect your home. A standard socket can handle up to 15-20 amps. That’s about 1800-2400 watts. Plugging in a generator can overload the socket. This is dangerous. It can cause fires. It can damage your home’s wiring.
- Check your generator’s output. It must match the socket’s capacity.
- Use heavy-duty sockets for high-power devices.
- Never bypass safety protocols. It’s not worth the risk.

Credit: www.cehjournal.org
Backfeeding Dangers
Exploring the topic of Backfeeding Dangers unveils a critical safety concern. This section dives into what backfeeding is and why it’s hazardous. Understanding these aspects is crucial for anyone considering plugging a generator into a wall socket.
What Is Backfeeding?
Backfeeding happens when power flows in the opposite direction. It occurs if someone connects a generator directly to a wall socket. This act forces power back into the utility lines. It’s like pushing water back up a hose.
Why Backfeeding Is Hazardous
Backfeeding poses several risks. Each risk underlines why this practice is dangerous:
- Electrocution risk: Utility workers may touch lines they believe are dead. Backfeeding can make these lines live without warning.
- Fire hazard: Incorrect connections can cause overheating. This overheating might start a fire in the home or at the utility pole.
- Damage to electronics: Backfeeding can create power surges. These surges can destroy electronics and appliances in the home.
- Legal issues: Many places have laws against backfeeding. Ignoring these laws can lead to fines or worse.
For these reasons, backfeeding is a practice to avoid. Always seek safer alternatives to power your home during an outage.
Legal And Code Considerations
Before plugging a generator into a wall socket, consider legal and code aspects. Building codes and potential legal repercussions guide this decision. Safety and legality are paramount.
Building Codes And Regulations
Local building codes dictate generator use. They ensure safety. These regulations vary by location. Always check local codes before using a generator this way.
- Electrical codes: Protect against fire and electrocution.
- Permits: Some areas require permits for generator installation.
- Installation standards: Dictate proper, safe connection methods.
Ignoring these codes can lead to penalties. It can also make your home unsafe.
Potential Legal Repercussions
Legal issues can arise from improper generator use. These include:
| Issue | Consequence |
|---|---|
| Damage to utility lines | Fines or liability for repairs |
| Unsafe conditions | Legal liability for injuries |
| Code violations | Fines and mandatory corrections |
To avoid these, follow all local laws and codes. Use a licensed electrician for installation. This ensures safety and compliance.
Proper Generator Connection Methods
Connecting a generator to your home requires safe methods. Safety is key to prevent accidents. You need the right equipment and knowledge. Below are the best ways to connect a generator.
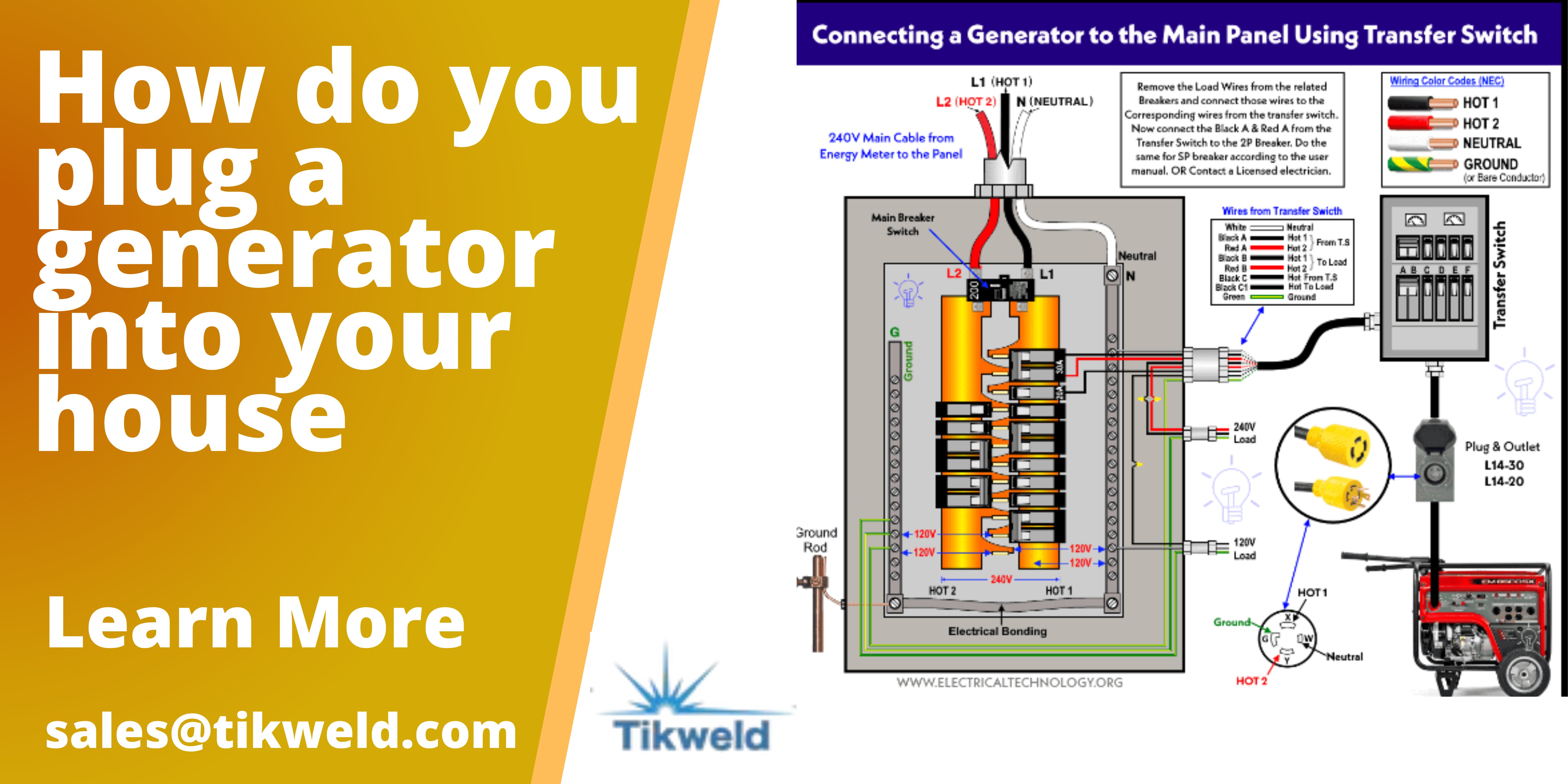
Using Transfer Switches
Transfer switches are a must for safe generator use. They connect generators to home circuits. This avoids backfeeding. Backfeeding is dangerous. It can harm utility workers and equipment.
- A transfer switch isolates selected circuits your generator will power.
- Professional installation is necessary. Electricians ensure everything is up to code.
- Manual and automatic transfer switches are available. Choose based on your needs.
Transfer switches make generator power manageable and safe. They are the recommended method by experts.
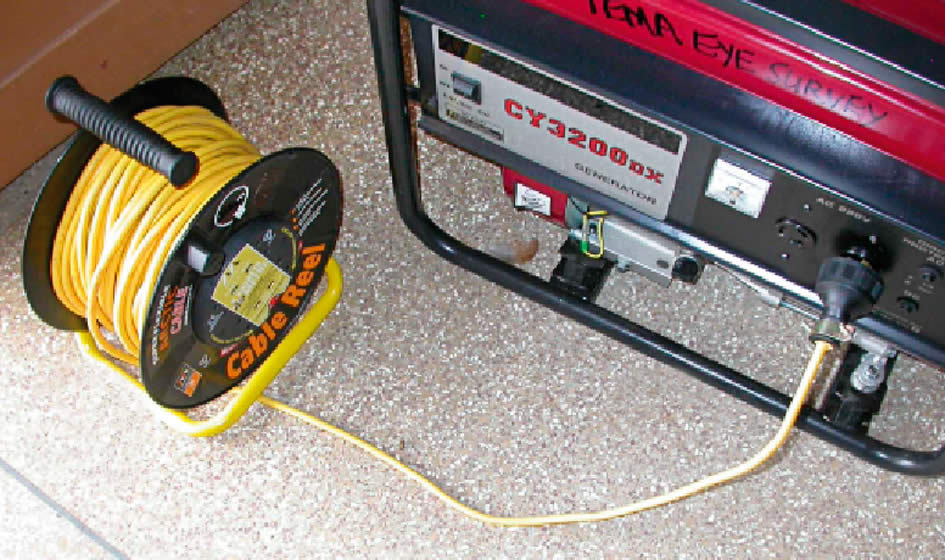
Extension Cord Safety
Extension cords offer a quick solution. They can be safe if used correctly. Always use heavy-duty, outdoor-rated cords. These are made for generator connections.
| Do’s | Don’ts |
|---|---|
| Use cords with a wattage rating above your generator’s output. | Don’t plug extension cords into each other. This can cause overheating. |
| Check for a grounding pin. It must be intact for safety. | Avoid running cords under carpets. This can create fire hazards. |
Keep cords away from water. They should be free of cuts and wear. Inspect them before each use.
Professional Installation And Safety
Professional Installation and Safety are critical when connecting generators to your home.
Never try to plug a generator into a wall socket without professional help. It can cause fires and electrocution.
Proper setup ensures your generator works well and keeps everyone safe.
Hiring A Qualified Electrician
An electrician makes sure your generator connects safely to your house.
They install a device called a transfer switch.
This switch keeps the generator from harming the power grid.
Find an electrician who knows local codes and can get permits if needed.
Routine Maintenance And Checks
Regular maintenance keeps your generator ready for emergencies.
Check the oil and filters often.
Run the generator monthly for at least 30 minutes.
Keep the area around the generator clear.
Always have extra fuel stored safely.

Credit: diy.stackexchange.com
Alternative Power Solutions
When the lights go out, being prepared matters. Alternative power solutions offer peace of mind. They keep your home humming during outages. Let’s explore some reliable options.
Uninterruptible Power Supplies
Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) are essential for short-term power needs. They jump into action when power cuts hit. They protect your devices from sudden shutdowns.
- Instant power for computers and networks
- Keeps data safe during brief outages
- Surge protection for electronics
Think of a UPS as your immediate go-to during sudden blackouts. They give you precious minutes to save work and shut down properly.
Solar Power And Battery Backups
Solar power shines with sustainability. It’s a long-term solution that harnesses the sun. Battery backups store this clean energy for later use.
| Benefits of Solar Power | Advantages of Battery Backups |
|---|---|
| Reduces electricity bills | Provides power during extended outages |
| Eco-friendly energy source | Stores solar or grid power for emergencies |
| Increases home value | Maintains power to critical devices |
Solar panels paired with battery systems offer resilience. They empower you against unpredictable weather and grid failures.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can You Safely Connect A Generator To Your Home?
Connecting a generator directly to your home’s electrical system without proper equipment is dangerous and can cause fires or electrocution.
What Is A Transfer Switch For Generators?
A transfer switch is a safety device that allows safe connection of a generator to your home’s electrical circuits, preventing back-feed.
Are Wall Sockets Suitable For Generators?
Wall sockets are not designed for generator connections as they can cause back-feed, risking damage to the electrical grid and injury.
What Risks Involve Plugging Generators Into Wall Sockets?
Plugging generators into wall sockets can lead to electrical back-feed, endangering utility workers, damaging appliances, and posing a fire hazard.
How To Properly Connect A Generator To Your House?
Hire a certified electrician to install a transfer switch, ensuring a safe and code-compliant connection of your generator to the home’s circuitry.
Conclusion
Wrapping up, plugging a generator directly into a wall socket isn’t a straightforward task. It demands caution, expertise, and proper equipment. Always prioritize safety and consult with a professional electrician to avoid hazardous situations. Remember, the right approach ensures reliability and peace of mind during power outages.





