For effective wound vac troubleshooting, first check the seal for leaks and ensure the device settings match the prescribed therapy. Examine the canister to confirm it isn’t full or improperly connected.
A wound vac, or vacuum-assisted closure device, plays a crucial role in modern wound care, promoting faster healing by applying negative pressure to draw edges of a wound together. It’s essential for healthcare professionals and patients alike to understand the basics of troubleshooting this equipment.
Issues can range from simple fixes like adjusting the vacuum’s intensity to more complex problems requiring professional intervention. By keeping an eye on common signs such as unexpected alarms or a noticeable decrease in suction, users can address problems swiftly, ensuring the therapy continues to support wound healing efficiently. This quick guide aims to demystify the process, making wound vac maintenance less intimidating and more manageable for all involved.
Introduction To Wound Vac Therapy
Introduction to Wound Vac Therapy marks a critical development in the healing of chronic and acute wounds. This modern medical approach uses controlled negative pressure to promote wound healing. The therapy aids in faster recovery by drawing out fluid from the wound and increasing blood flow to the area.
Purpose Of Wound Vac Systems
The purpose of Wound Vac systems lies in their ability to efficiently manage wounds. These devices:
- Remove excess fluids
- Reduce swelling
- Promote tissue growth
- Decrease bacterial load
Brief History Of Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (npwt)
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1990s | Introduction of NPWT |
| Early 2000s | Widespread adoption in hospitals |
| Today | Continued innovation and usage |
Common Wound Vac Systems
Vacuum-assisted closure of a wound involves controlled negative pressure. This method helps wounds heal faster. Several types of wound vac systems exist. Users must choose the right system for their needs. Understanding the common types of systems is crucial. Let’s explore these systems further.
Portable Vs. Stationary Models
Portable wound vacs offer flexibility and mobility. Patients can carry these devices with ease. Stationary models require a fixed position. Hospitals often use these for severe cases. Both models help wounds heal but serve different lifestyles.
Key Components And Their Functions
Every wound vac system includes essential parts. Each part plays a vital role in healing. Let’s break down these key components.
- Pump: Creates the negative pressure.
- Canister: Collects fluid from the wound.
- Dressing: Seals the wound and connects to the pump.
- Tubing: Links the dressing to the canister.
- Alarm System: Alerts for issues or full canisters.
Each component must work correctly for effective treatment. Regular checks ensure proper function. Troubleshooting is easier with knowledge of these parts.
Initial Setup Challenges
Setting up a Wound Vac can sometimes be tricky. Let’s talk about Initial Setup Challenges. Making mistakes during setup can slow down healing. But don’t worry! We will guide you through two main steps to make it easier.
Ensuring Proper Seal
Getting a good seal is key for a Wound Vac to work right. A good seal helps the device suck out fluid from the wound properly. Here are steps to ensure a proper seal:
- Clean the skin around the wound.
- Dry the area completely.
- Use a barrier film around the wound. Let it dry.
- Place the dressing carefully, making sure there are no wrinkles.
- Apply the adhesive film. Smooth it out for a tight seal.
This creates a strong seal, so the Wound Vac can do its job well.
Choosing The Right Dressing Kit
Using the right dressing kit is very important. The wrong one can hurt the wound or not work. Here’s how to choose the right kit:
- Look at the wound size. Pick a kit that fits well.
- Check the wound type. Some kits are for specific wounds.
- Ask a nurse or doctor if you’re not sure which to choose.
Choosing the right kit helps the Wound Vac heal the wound faster.

Credit: www.corkmedical.com
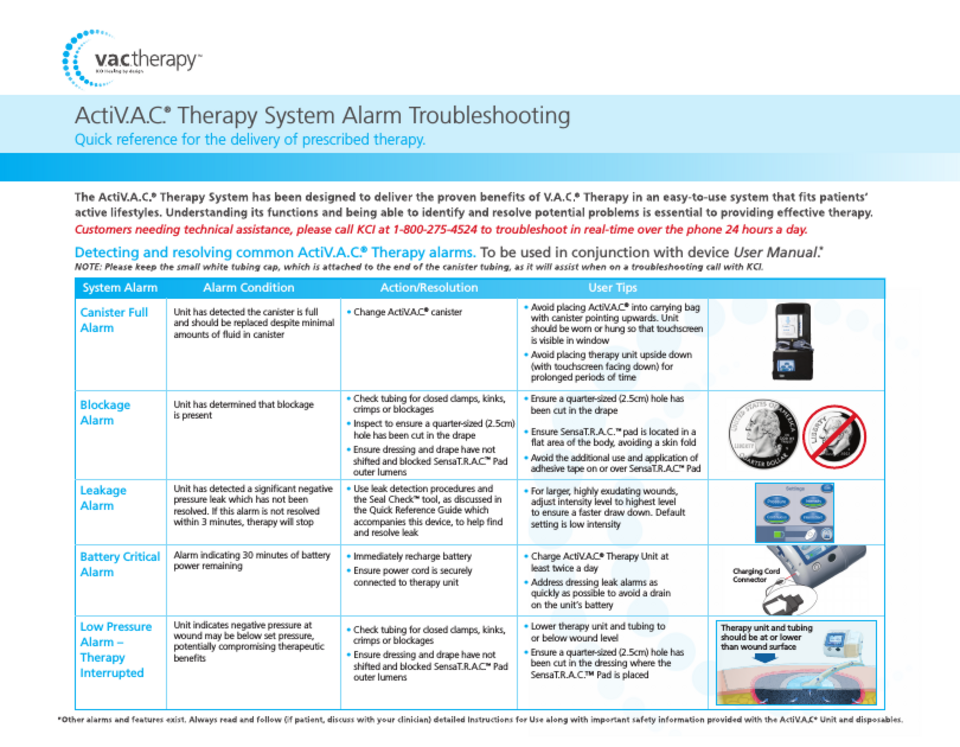
Addressing Alarm Signals
When managing wounds with a Vacuum-Assisted Closure (VAC) device, alarms play a crucial role. They alert caregivers to issues needing prompt attention. Understanding these signals ensures effective and safe wound care. Let’s delve into the types of alarms and steps to address them.
Interpreting Different Alarms
Wound VAC devices come with various alarms. Each alarm points to specific issues. Users must identify these to maintain therapy effectiveness.
- Low Pressure – Signals a leak in the dressing or tubing.
- High Pressure – Indicates a blockage or kink in the system.
- Battery – Warns of low power, requiring a charge or battery change.
- Canister Full – Notifies that the canister needs replacement.
Immediate Steps For Common Alarms
Quick action is essential when a Wound VAC alarm sounds. Follow these steps to address common alarms:
| Alarm Type | Action Required |
|---|---|
| Low Pressure | Check for leaks; ensure all connections are secure. |
| High Pressure | Inspect tubing for kinks; ensure the dressing is not too tight. |
| Battery | Connect to power or replace the battery. |
| Canister Full | Turn off the device; replace the canister. |
Leakage Issues And Solutions
Effective wound healing often relies on wound vacuums. Yet, leaks can hinder their performance. This section delves into common leakage issues and provides practical solutions.
Detecting The Source Of A Leak
Identifying a leak is the first step towards resolution. Users may hear an alarm or notice decreased suction. Inspect the dressing and tubing carefully. Search for gaps where the dressing meets the skin.
Effective Techniques To Resolve Leaks
Once a leak is detected, prompt action is crucial. Below are some effective techniques:
- Check the seal: Ensure the dressing adheres securely to the skin.
- Examine the tubing: Look for cracks or disconnections.
- Replace components: Swap out any damaged parts immediately.
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Dressing not sticking | Reapply or change the dressing |
| Loose connections | Secure all connections firmly |
| Full canister | Empty or replace the canister |
By following these steps, users can effectively manage and resolve leaks, ensuring the wound vac system operates efficiently for optimal healing.
Credit: www.bioclinicalservices.com.au
Managing Exudate And Fluid Levels
Managing exudate and fluid levels is crucial in wound care. A Wound Vac system helps in this process. Yet, sometimes, managing these levels can be challenging. Below, we explore ways to ensure optimal management and address abnormal levels.
Optimal Exudate Management
Optimal exudate management is key to healing. Here are steps to achieve it:
- Check the dressing regularly.
- Ensure a tight seal to prevent leaks.
- Adjust the vacuum’s settings as needed.
- Use appropriate dressing size.
These steps keep the wound environment ideal for healing.
What To Do When Fluid Levels Are Abnormal
Abnormal fluid levels can slow healing. Here’s what to do:
- Identify the cause of the abnormal level.
- Check for leaks in the dressing.
- Assess the wound and dressing condition.
- Consult a healthcare professional if unsure.
Addressing these issues promptly can help maintain the healing process.
Battery And Power Complications
Wound Vac systems rely on consistent power to aid healing. Battery and power issues can disrupt this process. Effective troubleshooting ensures the device operates smoothly.
Troubleshooting Power Failures
Power failures may halt wound therapy. Quick action is essential. Check the power cord and outlet first. Ensure the device plug fits securely. A loose connection can cause interruptions. If the issue persists, inspect the power adapter. Damage here may need professional attention.
- Examine the power cord and outlet.
- Secure the device plug firmly.
- Assess the power adapter for damage.
- Seek professional help for adapter issues.
Maintaining Battery Life
Long battery life is crucial for uninterrupted healing. Charge the battery regularly. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for charging cycles. Avoid overcharging; it reduces battery lifespan. Store the device at moderate temperatures. Extreme heat or cold impacts battery performance.
- Charge the battery as directed.
- Do not overcharge the battery.
- Keep the device at room temperature.
| Do | Don’t |
|---|---|
| Follow charging instructions | Overcharge the battery |
| Store at moderate temperatures | Expose to extreme conditions |

Credit: woundreference.com
Infection Control And Prevention
Infection control and prevention is crucial in wound care. Ensuring a wound remains free from infection is key for healing. Wound vacs assist in this process but require careful management. This section covers steps to identify signs of infection and maintain a sterile environment.
Identifying Signs Of Infection
Recognizing an infection early can prevent complications. Look out for:
- Redness around the wound site
- Increase in wound size or depth
- Foul odor emanating from the wound
- Discharge that is yellow, green, or brown
- Fever or chills indicating a systemic infection
Sterilization And Cleaning Protocols
Proper care for wound vac systems is vital. Follow these steps:
- Wash hands before and after touching the vac or wound area.
- Use gloves to prevent contamination.
- Clean all wound vac components as instructed by the manufacturer.
- Replace filters and canisters regularly to maintain sterility.
- Check for any leaks in the system that may introduce pathogens.
Patient Comfort And Wound Vac Use
Ensuring patient comfort is crucial when using a Wound Vac. This therapy helps wounds heal faster. Yet, for some, it can be uncomfortable. Making this process as pain-free as possible is key. Let’s explore ways to minimize discomfort and educate patients about their Wound Vac treatment.
Minimizing Discomfort During Therapy
To reduce pain and discomfort during Wound Vac therapy, follow these tips:
- Check the dressing: Secure but not too tight.
- Maintain the seal: Prevents leaks and maintains suction.
- Adjust the pressure: Match the doctor’s prescription.
- Medicate if necessary: Use pain relief as prescribed.
- Reposition regularly: Reduces pressure on the wound area.
Comfort is vital for healing. With the right approach, Wound Vac therapy can be more bearable.
Educating Patients About Wound Vac Use
Education is key for successful Wound Vac therapy. Here’s how to inform patients:
- Explain the process: Helps patient understand the treatment.
- Discuss benefits: Encourages patient cooperation.
- Demonstrate use: Shows how to manage the device at home.
- Provide resources: Gives access to helpful information.
- Offer support: Ensures questions are answered promptly.
With knowledge and support, patients can navigate their Wound Vac therapy confidently.
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques are vital for maintaining Wound Vac systems. These techniques can tackle complex issues that basic steps can’t fix. Let’s dive into sophisticated methods to keep your device in top shape.
Dealing With Complex Wound Scenarios
Some wounds present unique challenges. Here are steps to manage them:
- Check seal integrity: Ensure the dressing is airtight.
- Monitor exudate type: Adjust settings based on fluid thickness.
- Assess wound size regularly: Change treatment plans as needed.
- Use specialized dressings: Fit for the wound’s shape and depth.
Remember to document changes and effects after each adjustment.
When To Seek Professional Technical Support
Some situations require expert help:
- Continuous error messages: Device may need repair or replacement.
- Persistent leaks: Could signal a malfunction.
- Unusual noises: May indicate internal issues.
- Changes in wound appearance: Seek medical advice immediately.
Contact the device manufacturer or healthcare provider for assistance.
Maintenance And Care Of Wound Vac Equipment
The right maintenance and care for Wound Vac equipment are vital. They ensure effective treatment and extend the system’s life. This section covers essential tips and a checklist for keeping the Wound Vac in top condition.
Regular Maintenance Checklist
- Inspect the equipment daily for signs of wear.
- Check the seal around the dressing for leaks.
- Review the canister for filling and proper connection.
- Listen for abnormal sounds from the pump.
- Clean the exterior with a soft, damp cloth.
- Replace filters and batteries as recommended.
Longevity Tips For Wound Vac Systems
Keep your Wound Vac system running longer with these tips:
| Tip | Action |
|---|---|
| Storage | Keep in a clean, dry place when not in use. |
| Handling | Carry with care; avoid dropping or jarring. |
| Charging | Follow the manufacturer’s instructions. |
| Dressings | Use compatible materials and change as directed. |
| Documentation | Track maintenance and treatment records. |
Conclusion: Best Practices For Effective Wound Vac Therapy
Wound Vac Therapy helps wounds heal faster and better. This therapy needs care and knowledge for the best results. We will share tips and tricks to make Wound Vac Therapy work well.
Summarizing Key Troubleshooting Points
- Check the seal often. A good seal stops leaks.
- Listen for alarms. They tell you if something is wrong.
- Clean the area around the wound carefully.
- Change the dressing as told by the doctor.
- Keep the equipment clean. This stops infections.
Continual Learning And Adaptation
Learning never stops with Wound Vac Therapy. Each wound is different. So, the way you care for it may change.
- Read up on new Wound Vac methods.
- Go to training sessions.
- Talk to others who use Wound Vac. Share tips.
- Ask doctors or nurses when unsure.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is A Wound Vac?
A wound vac, or vacuum-assisted closure, helps wounds heal by applying negative pressure to draw out fluid and increase blood flow to the area.
How To Resolve Wound Vac Alarm Issues?
Check the device connections for leaks, ensure the dressing is sealed properly, and consult the user manual for specific alarm codes.
Why Is My Wound Vac Not Sticking?
Ensure the wound area is dry before application, use an appropriate adhesive barrier, and confirm that the dressing size is adequate for coverage.
Can I Shower With A Wound Vac?
Typically, a waterproof cover is required to protect the Wound Vac during showering; consult your healthcare provider for specific instructions.
How Often To Change Wound Vac Dressings?
The frequency of dressing changes varies; however, most protocols suggest every 48 to 72 hours, unless otherwise directed by a healthcare professional.
Troubleshooting Wound Vac Low-pressure Error?
Inspect the dressing and tubing for leaks, ensure a proper seal, and check the device’s canister to ensure it’s not full and needing replacement.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of wound vac systems can be daunting. Yet, with the insights shared, users are better equipped to handle common issues. Remember, proper maintenance and following manufacturer guidelines are key to smooth operation. Should challenges arise, consult a healthcare professional to ensure optimal healing and care.





